
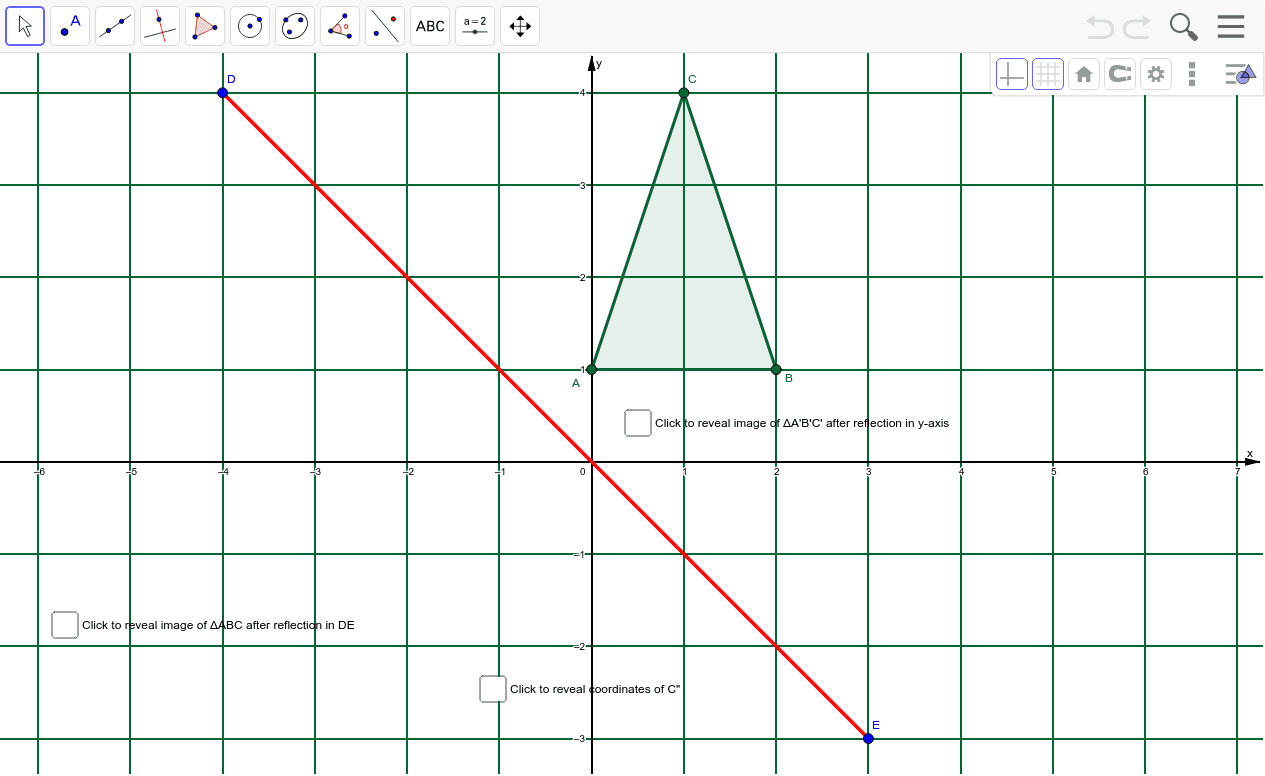
#Reflection on y axis function series#
The basic purpose of composing transformations is to gain efficiency by applying a single composed transformation to a point, rather than applying a series of transformation, one after another.įor example, to rotate an object about an arbitrary point (X p, Y p), we have to carry out three steps − The change in the order of transformation would lead to different results, as in general matrix multiplication is not cumulative, that is. This is written as T = T1∙T2.Ĭomposite transformation can be achieved by concatenation of transformation matrices to obtain a combined transformation matrix. If a transformation of the plane T1 is followed by a second plane transformation T2, then the result itself may be represented by a single transformation T which is the composition of T1 and T2 taken in that order. The Y-Shear can be represented in matrix from as − The Y-Shear preserves the X coordinates and changes the Y coordinates which causes the horizontal lines to transform into lines which slopes up or down as shown in the following figure. The transformation matrix for X-Shear can be represented as − The X-Shear preserves the Y coordinate and changes are made to X coordinates, which causes the vertical lines to tilt right or left as shown in below figure. However in both the cases only one coordinate changes its coordinates and other preserves its values. One shifts X coordinates values and other shifts Y coordinate values. There are two shear transformations X-Shear and Y-Shear. ShearĪ transformation that slants the shape of an object is called the shear transformation. The following figures show reflections with respect to X and Y axes, and about the origin respectively. In reflection transformation, the size of the object does not change. In other words, we can say that it is a rotation operation with 180°. Reflection is the mirror image of original object. If we provide values greater than 1, then we can increase the size of the object. If we provide values less than 1 to the scaling factor S, then we can reduce the size of the object. The scaling process is shown in the following figure. The above equations can also be represented using the column vectors. The pair (t x, t y) is called the translation vector or shift vector. You can translate a point in 2D by adding translation coordinate (t x, t y) to the original coordinate (X, Y) to get the new coordinate (X’, Y’).įrom the above figure, you can write that − TranslationĪ translation moves an object to a different position on the screen. Any Cartesian point P(X, Y) can be converted to homogenous coordinates by P’ (X h, Y h, h). In this system, we can represent all the transformation equations in matrix multiplication. In this way, we can represent the point by 3 numbers instead of 2 numbers, which is called Homogenous Coordinate system. To convert a 2×2 matrix to 3×3 matrix, we have to add an extra dummy coordinate W. To shorten this process, we have to use 3×3 transformation matrix instead of 2×2 transformation matrix. Scale the rotated coordinates to complete the composite transformation.Rotate the translated coordinates, and then.
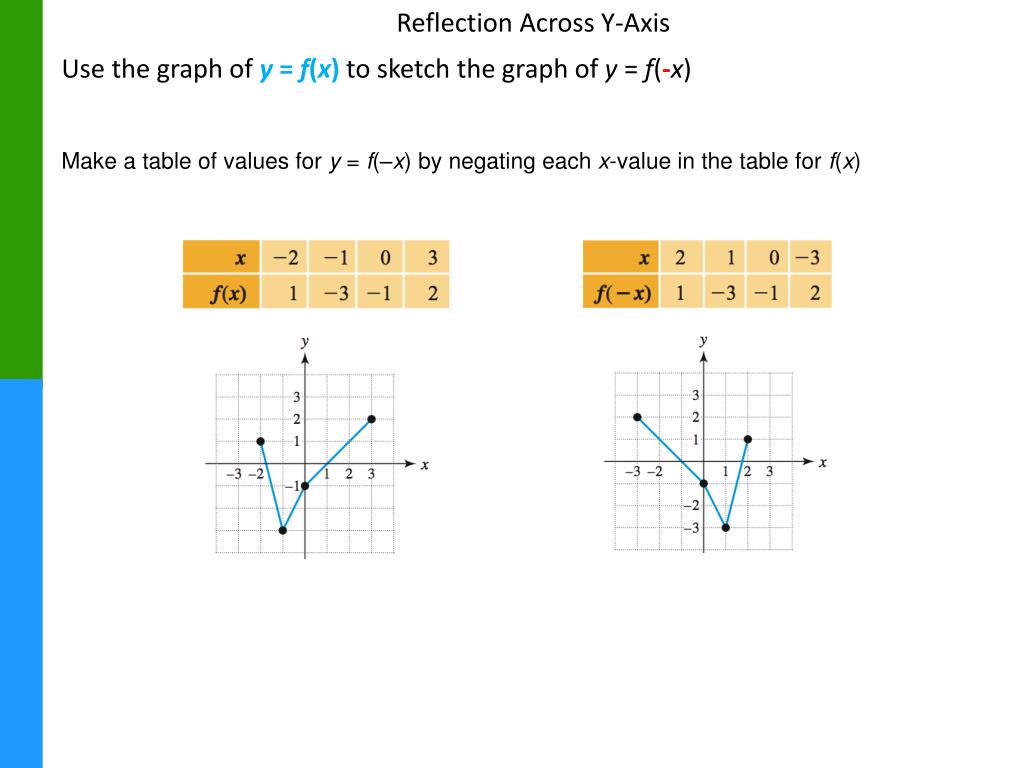
To perform a sequence of transformation such as translation followed by rotation and scaling, we need to follow a sequential process − Transformations play an important role in computer graphics to reposition the graphics on the screen and change their size or orientation. When a transformation takes place on a 2D plane, it is called 2D transformation. We can have various types of transformations such as translation, scaling up or down, rotation, shearing, etc. Transformation means changing some graphics into something else by applying rules.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
